The tundra biome is one of the most unique and challenging ecosystems on our planet. It is characterized by cold temperatures, permafrost, and a short growing season. Despite these challenges, the tundra supports a diverse range of plant and animal life, and understanding the food chain is essential to preserving this delicate ecosystem. In this article, we will explore the tundra food chain, from the primary producers to the top predators.
1. Introduction
The tundra is a vast and desolate landscape, but it is teeming with life. The food chain is the backbone of this ecosystem, and it starts with the primary producers. Understanding how each organism in the food chain is connected is essential to understanding the complex tundra biome.
2. What is a Food Chain?
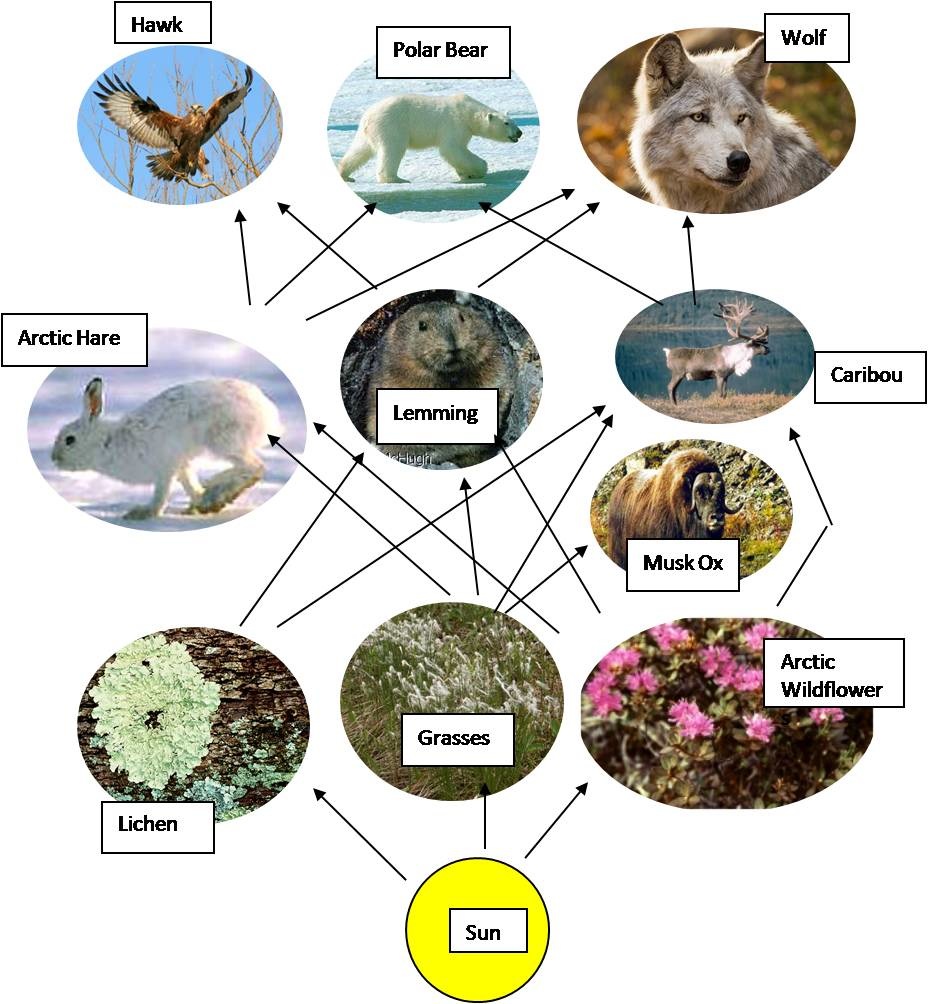
A food chain is a series of organisms that are interdependent on each other for food. The energy from the sun is captured by plants, which are then eaten by herbivores. The herbivores are then eaten by carnivores, and the cycle continues.
3. Tundra Biome: An Overview
The tundra is a vast biome that covers much of the Arctic and subarctic regions of the world. It is characterized by low temperatures, permafrost, and a short growing season. The tundra is divided into two types: Arctic tundra and alpine tundra.
4. Primary Producers: Mosses, Lichens, and Grasses
The primary producers in the tundra are mosses, lichens, and grasses. They are adapted to the harsh environment and can survive in the cold temperatures and low light. They are the base of the food chain and provide energy to the herbivores.
5. Herbivores: Lemmings, Hares, and Caribou
Lemmings, hares, and caribou are the primary herbivores in the tundra food chain. They feed on the primary producers and are adapted to survive in the cold temperatures. They are an essential food source for the carnivores in the tundra.
6. Omnivores: Arctic Foxes and Brown Bears
Arctic foxes and brown bears are omnivores in the tundra food chain. They feed on both plants and animals and are an important link between the herbivores and the top predators. They are well adapted to survive in the harsh environment of the tundra.
7. Top Predators: Wolves and Polar Bears
Wolves and polar bears are the top predators in the tundra food chain. They hunt and feed on the herbivores and the omnivores in the tundra. They are apex predators and play a vital role in controlling the population of the herbivores and the omnivores.
8. Scavengers: Ravens and Bald Eagles
Ravens and bald eagles are scavengers in the tundra food chain. They feed on the remains of dead animals.
9. Decomposers: Bacteria and Fungi
Decomposers are an essential part of the food chain in the tundra. Bacteria and fungi break down dead organic matter and recycle nutrients back into the soil, which are used by the primary producers. Without decomposers, the tundra ecosystem would not be sustainable.
10. Human Impact on the Tundra Food Chain
Human activities, such as oil drilling, mining, and pollution, have a significant impact on the tundra food chain. These activities can disrupt the delicate balance of the ecosystem, which can lead to a decline in the population of certain species and ultimately affect the entire food chain.
11. Conservation Efforts
Conservation efforts are crucial to preserving the tundra ecosystem and its food chain. Governments, scientists, and organizations are working together to minimize human impact on the tundra, protect endangered species, and promote sustainable practices that support the food chain.
12. Conclusion
The tundra food chain is a complex and delicate ecosystem that plays a vital role in the survival of many species. Understanding the food chain is essential to preserving the tundra biome and its inhabitants. By taking steps to minimize human impact and promote conservation efforts, we can ensure that the tundra food chain continues to thrive for generations to come. Read more: Travel Malang Jember
13. FAQs
What is the primary producer in the tundra food chain?
The primary producers in the tundra food chain are mosses, lichens, and grasses.
What is the role of decomposers in the tundra ecosystem?
Decomposers break down dead organic matter and recycle nutrients back into the soil, which are used by the primary producers.
What are the top predators in the tundra food chain?
The top predators in the tundra food chain are wolves and polar bears.
How does human activity affect the tundra food chain?
Human activities, such as oil drilling, mining, and pollution, can disrupt the delicate balance of the tundra ecosystem, which can lead to a decline in the population of certain species and ultimately affect the entire food chain.
What can be done to preserve the tundra food chain?
Conservation efforts, such as minimizing human impact and promoting sustainable practices, are crucial to preserving the tundra food chain and its inhabitants.






